Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a groundbreaking new technology that could transform food safety and detection. The team, led by Prof. Huang Qing, has created a series of Cu metal-organic framework (MOF) nanozymes that mimic the activity of laccase, a natural enzyme. These nanozymes exhibit varying responses to common bioactive substances found in food, enabling highly sensitive and rapid identification and quantitative analysis of these components. The researchers have also developed encoded array sensors that can be easily observed using a smartphone, revolutionizing portable and intelligent food detection. This innovative approach not only provides a new way to prepare efficient nanozymes but also offers an intelligent and convenient method for food inspection.
Unlocking the Potential of Nanozymes
Introduction Nanozymes have found their own place in the world of detection and are considered significant due to their high catalytic activity, stability, and ease of being designed by researchers. Efficient nanozymes, built or prepared by the researchers, create novel sensors and promising diverse applications such as for food detection.
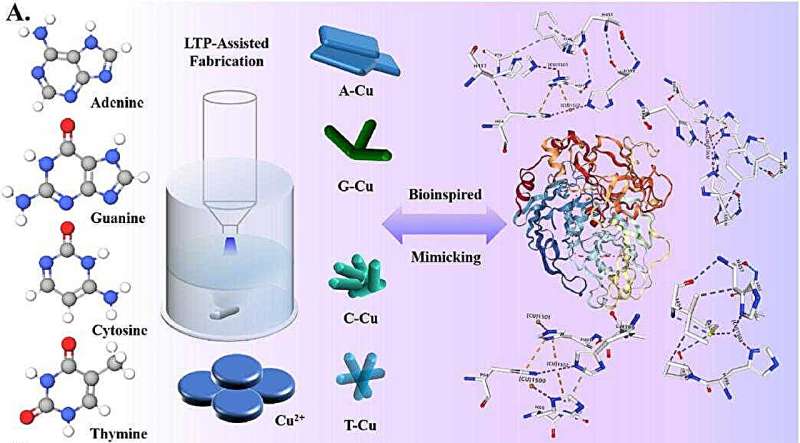
Prof. Huang Qing’s team of collaborators has devised a novel way to make their Cu-MOF nanozymes. In their study, the researchers prepared a series of nanozymes with various base ligands using gas-liquid interface dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) low-temperature plasma (LTP) technology. Unlike natural laccase, these nanozymes model how the enzyme works to help regulate food processing and quality.
In this work, the researchers successfully proven that these nanozymes can selectively response to five kinds of bioactive components from foods, which endows them with potential for smart and high-sensitive food detection. Using encoded array sensors they have built a system that can rapidly and sensitively recognize the compounds as well as measure their amounts down to mere parts-per-billion.
AI-Powered Handheld Food Scanner
Darkfield image of encoded array sensors detecting NO2 gas using a smartphone (scale bar = 1cm).This research has focused on the development of encoded large-area sensors that are readily observed through a smartphone. This new technology underlines a portable and smart rapid food detection system helps shape the manner of how we treat the research of food safety and quality control.
This will allow identifying nanozyme-catalyzed color development, which can be detected and quantitatively analyzed by a smartphone-based visible-light specrophotometer. This supports the possibility of testing while on-the-go and in real-time monitoring of products, which can benefit consumers just as much if not more than food producers.
These sensors can detect and quantify substances in the concentration range of 1.5–150 μg/mL, which is both wide and sensitive, and have detection limits as low as 1.4 ± 0.3 µg/ml for Cu2+ ions or minimum values lower than that across other studies [15]. This high level of technology not only greatly facilitates the discovery process but also makes more reliable and accurate measurements, guaranteeing then above all the security and quality of our food supply.
Opening a New Chapter in Food Maintenance
If realized, the innovative sensor technology using this Cu-MOF nanozyme could be a game-changer in food inspection and safety.
The smart, simple and portable method designed by the researchers to identify and quantify critical bioactive substances in the food industry. This feature is important in identifying different additives, pollutants and other substances influencing the quality and safety of food products.
In addition, the versatility of these tailorable nanozymes in sensing different biologically active molecules extends their ease of use for deployment to various applications within food industry. While this technology continues to be improved upon and furthered by the researchers, one finds oneself looking forward to what more awaits in the absolutely absorb field of smart diet detection.
In sum, this innovative research constitutes a great stride towards advancing in food safety and quality control. Using the nanocoated nanozymes and intelligent sensor system for food inspection, these researchers from this team have opened a new chapter in intelligent agriculture with broad applicability to both consumers and industry.
