Researchers from Kyushu University in Japan have uncovered a remarkable calcium-based mechanism that plays a crucial role in the disposal of dead cells, shedding light on how our bodies protect themselves from injury and disease. This discovery has profound implications for understanding and potentially treating conditions related to epithelial barrier disruption, such as atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease.
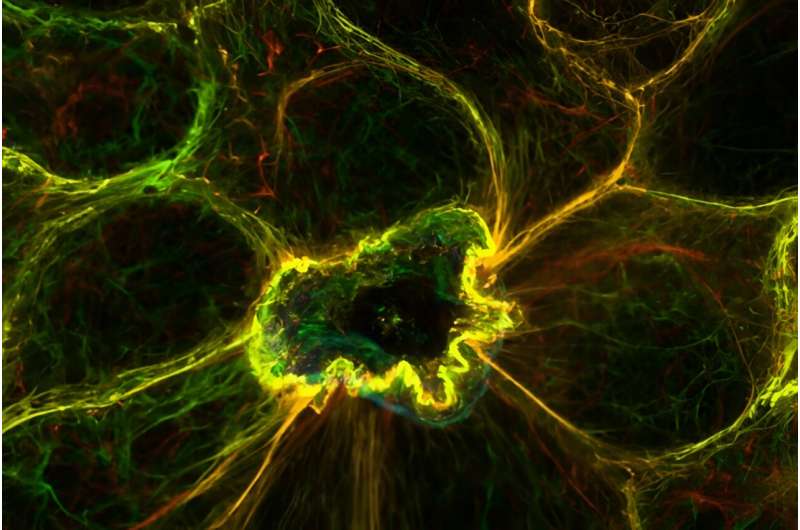
Role of Calcium in Ensuring the Removal of Dead Cells
The human body is an amazing thing, with complicated machinery running day in and day out to keep us alive and well. An example of such a crucial mechanism is that of the elimination of unhealthy or dead cells, important to keep our epithelial tissues —the physical borders inside organs and which cover both outer and inner surfaces—intact.
A research team at Kyushu University led by Prof Junichi Ikenouchi and colleagues has discovered a novel calcium-mediated cyst exit mechanism during efferocytic process (engulfing and removing of apoptotic cells) With the help of sophisticated methods to genetically engineer epithelial tissue cultures, molecular markers and high-resolution imaging, researchers have shown that calcium plays a pivotal role in this intricate but life-sustaining task.
When a cell dies by apoptosis, the nearby cells show sustained extremely high levels of calcium but generally more locally close to where they abut the dying cell. Referred to as the “calcium response in effectors of apical extrusion (CaRE)”, this anomaly is at the heart of a new mechanism that has now been unravelled.
Desmosomes: The Ones who Make Extrusion Happen
Subsequent investigation by the research team then revealed the critical involvement of desmosomes in this calcium-dependent cellular removal process. Desmosomes are a specific type of cell adhesion structure (adherens juctions, gap junctiosn) that function as buttons between cells to fasten them in place (like Velcro) and keep the architecture of our epithelial tissues in-check.
According to the researchers, this activation occurs at or near desmosomes and is a coincidence in space and time with their data on the force transduced from conformed if not contracted actomyosin complex (the molecular machine that allows cells to move and change their shape). This contraction — mediated by the calcium response ( Movie 1 in S2 Movie ) — allows the adjacent cells to expel the apoptotic cell and close any breaches without disturbing the integrity of the epithelial sheet.
This finding contradicts the common idea that desmosomes are responsible only for mechanical coupling between cells. These findings identified a novel function of these adhesion structures in the calcium dependent cell disposal process, revealing the fascinating complexity and adaptability of our body’s defense mechanisms.
Consequences for Epithelial Disease Pathology
The discovery made by the team has implications that go well beyond cell biology. The team indicates that this fresh calcium-dependent apoptotic cell efferocytosis reveals to develop more effective therapy and prevention approaches for various epithelial barrier-associated diseases.
The findings from this study could also shed light on understanding and treating diseases such as atopic dermatitis or inflammatory bowel disease, where the epithelial barrier is impaired. Understanding the precise interplay between these elements of calcium, desmosomes, and actomyosin complex may be helpful in developing distinct interventions that promote a more effective clearance/removal of defective cells therefore allowing for repair & integrity to an epithelial barrier.
Ultimately, more testing is required to identify how the CaRE mechanism may work in living organisms, its range among various organ tissues, and possibly involve other factors — all which would allow scientists to draw a much clearer image of the function of diversity in biology. However, in terms of our truly incredible ability to heal ourselves, this study is a big deal; it opens the door for creative interventions that could help treat many epithelial-based health conditions.
