Researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of quantum computing. Their innovative approach using high-dimensional spatial encoding has the potential to overcome scalability and computation duration issues, paving the way for faster and more efficient quantum computers. This research, published in Nature Photonics, marks a significant milestone in the quest to harness the full potential of quantum technology.
Scale of Quantum Computation with Spatial Encoding
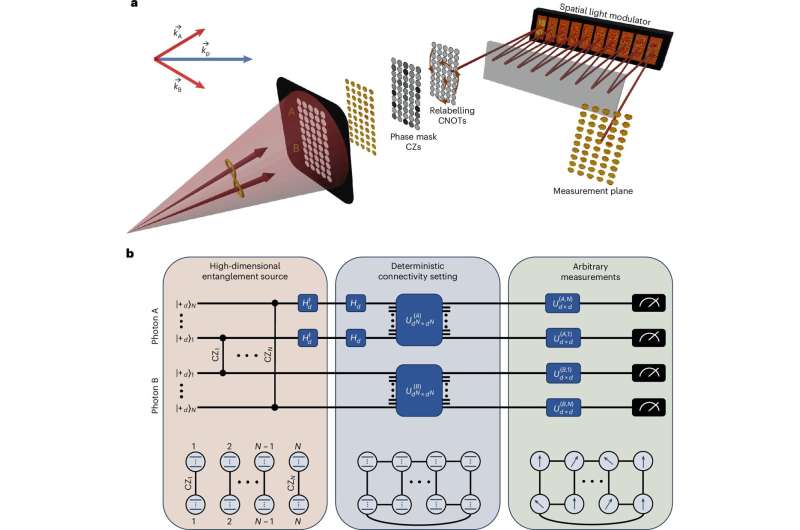
Up to now, the biggest bottleneck in quantum computing was the production of strong cluster states for computation. The standard approach has low detection probabilities that fall off exponentially with the number of photons. Yet, a nascent approach for circumventing this obstacle was developed by Yaron Bromberg and Ohad Lib of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
In their landmark paper, published in Nature Photonics, the researchers describe how they are now using high-dimensional spatial encoding to produce large cluster states. Using the time and frequency degrees of freedom, this group has managed to create cluster states well beyond nine qubits at the 100 Hz rate by encoding multiple qubits in each photon. It is a huge milestone in making quantum computing more scalable and addressing some of its biggest challenges.
Enhancing the efficiency of quantum computation
The researchers’ approach also helps solve the problem of computation duration, in addition to scalability. This method harnesses photons as intermediaries and by encoding multiple qubits in a single photon the speed of computational raiding between qubits is reduced to effectively zero.
This development represents a game changer for the field of quantum computing. In other words, as Prof. Bromberg clarifies: “Our findings prove that utilizing large-dimensional encoding solves existing issues about scalability of quantum computers, while providing a practical and efficient way for scaling up the computational power provided by a quantum computation.scheme.” It’s a major step forward. The approach by Dr. Lib (middle), ” addresses both scalability and computation duration difficulties, pointing toward a measurement-based future direction of quantum computing. Upshot: The age of quantum technology is now that much closer.
Facilitating a road for Quantum Computers immune to failures
The research has vast implications, The way is now open for more efficient quantum computations by resolving the major bottleneck in scalability and duration of computation using the new photonics method. That could help usher in the era of faster, fault-tolerant quantum computers designed to tackle problems that are currently beyond the capacity of classical computers.
The research group reports that the study is a critical step toward unlocking the full promise of quantum computing through photonics. The paper argued that quantum computers could grow vastly more powerful and efficient in the very near future, thanks to some new work by physicists. The breakthrough is a testament to some of the best and brightest in the annals of quantum computing.
