Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a novel detection technology that can rapidly identify toxic metabolites derived from 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), providing valuable health warnings and risk assessments. This breakthrough has the potential to transform workplace safety and environmental monitoring, particularly in industries involving TNT production. TNT and its metabolites pose significant health risks, making their detection critical.
Unlocking the Secrets of Toxic TNT Metabolites
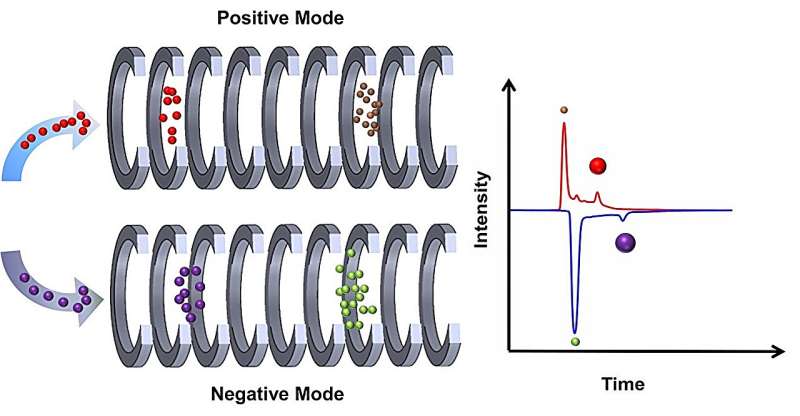
The research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an innovative approach to detect both positive and negative ions of four hazardous metabolites derived from TNT. These metabolites, including 2-amino-4,6-dinitrotoluene (2-ADNT), 4-amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene (4-ADNT), 2,4-diamino-6-nitrotoluene (2,4-DANT), and 2,6-diamino-4-nitrotoluene (2,6-DANT), pose significant health risks to workers in TNT manufacturing facilities and the general population.
The researchers utilized a cutting-edge technology called dual drift tube ion mobility spectrometry (DDT-IMS) to rapidly detect these metabolites. This method allowed them to analyze the ion mobility of the metabolites and understand how drift tube temperature affects the detection results. By applying this technology to urine samples, the team demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of DDT-IMS in identifying TNT metabolites within complex biological matrices.
Transforming Workplace Safety and Environmental Monitoring
The development of this novel detection technology has far-reaching implications for workplace safety and environmental monitoring. TNT and its metabolites are not only hazardous to human health but also pose a significant threat to the environment. The ability to quickly and accurately detect these compounds can help mitigate the risks associated with TNT exposure, particularly in industries where it is manufactured or used.
According to Professor Huang Chaoqun, the lead researcher of the HFIPS team, this technology has the potential to transform the way we assess the environmental and biological risks of TNT. By providing rapid and reliable detection of TNT metabolites, it can enable early intervention and preventive measures, ensuring the well-being of workers and the surrounding communities.
Empowering Informed Decision-Making and Risk Management
The availability of this novel detection technology can empower employers, policymakers, and public health authorities to make more informed decisions and implement effective risk management strategies. By accurately identifying the presence and levels of TNT metabolites, they can take proactive steps to mitigate exposure, implement stricter safety protocols, and monitor the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
Moreover, this technology can contribute to a deeper understanding of the long-term health impacts of TNT exposure, leading to the development of targeted interventions and improved occupational and environmental regulations. As the research team continues to refine and expand the applications of DDT-IMS, it holds the promise of enhancing workplace safety, protecting public health, and safeguarding the environment for generations to come.
