During the pandemic, many turned to making sourdough bread as a hobby. Studies show its nutritional benefits, including higher vitamins and minerals compared to regular bread. Scientists at Syracuse University explored the genetic diversity of acetic acid bacteria (AAB) in sourdough starters, revealing their impact on flavor and health benefits. The research, published in mSystems, could revolutionize sourdough baking and have far-reaching implications for human health and environmental sustainability.
Microbiomes of Sourdough
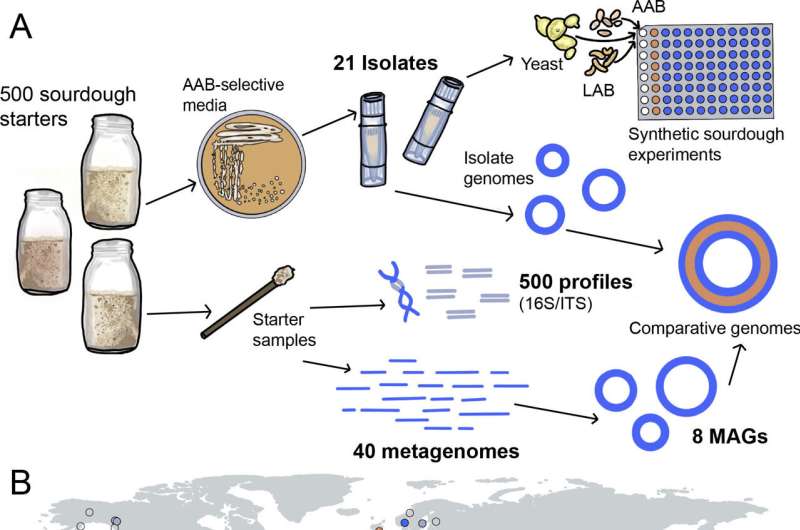
Sourdough is made through a long fermentation using the wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria endemic to the flour, air, and grain stored in local communities. In fact, AAB in sourdough starters have been studied for understanding their genetic diversity and implication on[/have a] dominant flavor and health benefits ; It could change the way we think about making sourdough.
- Sudough batter microbial community
- Acetic acid bacteria-vcariablencs of divers genotypcs
- Effects of Flavor and Health Pros
Benefits on health and taste formation
Acetic acid bacteria (AAB) are essential components of sourdough, contributing to flavor and health benefits. The research revealed that distinct AAB strains excrete different flavoring molecules, which may alter the taste of sourdough bread. In the end, this can allows bakers to adjust flavor and texture in sourdough in a way that they were unware of before.
- AAB Contribution to Flavor Formation
- Influencing the taste and texture of sourdough
- The medicinal properties of AAB in sourdough
Human Health Implications and beyond
Their recent research also reveals that a study on sourdough microbial diversity extends beyond baking, having implications into whether they enter the human health and environmental sustainability fields. Studying the variety of strains within microbial communities is critical for optimizing human and environmental microbiomes. It showed that a little chemistry will go a long way in improving human health and environmental sustainability.
- Strain-level differences in communities of microorganisms
- Effect on Human health and environment sustainability
- Improvements with health and sustainability
