Researchers have discovered a new way to detect and monitor radiation-induced lung damage using advanced imaging techniques called radiomics. By analyzing detailed patterns in CT scans of the lungs, they were able to accurately identify animals that had been exposed to radiation, as well as those treated with stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles to mitigate the damage. This non-invasive approach could lead to earlier detection and better management of lung toxicity in cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. The findings highlight the potential of radiomics to uncover subtle changes in tissue that may be missed by traditional imaging methods.
Uncovering the Hidden Impact of Radiation on the Lungs
Radiation therapy is a critical tool in the fight against cancer, but it can also cause significant damage to healthy tissues like the lungs. This radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a major concern for patients receiving thoracic radiation, and can lead to debilitating and even life-threatening complications. Finding ways to accurately detect and monitor RILI is crucial for improving cancer treatment outcomes.
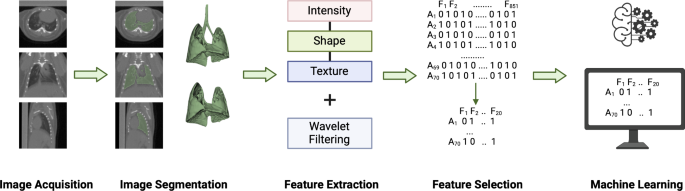
Enter radiomics – an emerging field that uses advanced computational analysis to extract detailed quantitative information from medical images. By analyzing features like intensity, texture, and shape in CT scans, radiomics can uncover subtle patterns that may reveal important insights about tissue structure and function.
Putting Radiomics to the Test
In a recent study, researchers set out to investigate whether radiomics could be used to identify RILI in an animal model. They exposed mice to different doses of radiation, either to the whole lung or just a specific region, and then monitored the animals using cone-beam CT scans.
When the researchers looked at simple measurements of lung density, they didn’t see any significant differences between the irradiated and control groups. However, when they delved deeper into the radiomics data, a different story emerged.

Revealing Radiation-Induced Changes with Radiomics
Using a machine learning approach, the researchers were able to train models that could accurately predict whether an animal had been exposed to radiation, as well as whether they had received stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) to potentially mitigate the damage.
The radiomics analysis revealed several key features that were altered in the irradiated lungs, including changes in texture and intensity patterns. Interestingly, the researchers also found that the radiomics signature could detect a protective effect of the EV treatment, even in the locally irradiated lungs – something that wasn’t apparent from the simple density measurements.
A Promising Path Forward
This study demonstrates the power of radiomics to uncover subtle, but clinically relevant, changes in lung tissue following radiation exposure. By going beyond traditional imaging metrics, the researchers were able to develop sensitive and reliable biomarkers of RILI that could be used to guide treatment decisions and monitor the efficacy of interventions.
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to further validate their radiomics approach in larger studies, and explore how it might be applied to improve the care of cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. With the potential to detect lung damage earlier and more accurately, radiomics could play a crucial role in minimizing the adverse effects of this life-saving treatment.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Olivia G. G. Drayson, Pierre Montay-Gruel, Charles L. Limoli.
For More Related Articles Click Here
