
Maintaining the health and stability of wild ungulate populations is a critical challenge for wildlife conservation. A recent study by a team of researchers has shed light on how the gut microbiome of wild red deer (Cervus elaphus) responds to changes in their nutritional status during the harsh winter months. By analyzing the gut microbes and nutritional indicators of both wild and captive red deer, the researchers uncovered fascinating insights into the complex relationship between an animal’s diet, its gut bacteria, and its overall well-being. This study provides valuable information that could help wildlife managers better understand and support the resilience of these important forest ecosystem inhabitants. Red deer, gut microbiome, nutritional status, wildlife conservation
Navigating the Harsh Winters of the Northern Forests
In the northern forests of China, wild ungulates like the red deer face significant challenges during the winter months. Low temperatures, limited plant resources, and poor food quality can all contribute to nutritional deficiencies that threaten the health and survival of these animals. Understanding how wild red deer adapt to these harsh conditions is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
Gut Microbes: A Window into Nutritional Status
The gut microbiome, the diverse community of microorganisms that reside in an animal’s digestive tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining nutritional balance. Previous studies have shown that changes in an animal’s nutritional status can lead to abrupt alterations in its gut microbiome. By analyzing the gut microbes of wild red deer, the researchers aimed to uncover potential indicators of nutritional stress that could inform wildlife management efforts.
Tracking Nutritional Changes in Wild Red Deer
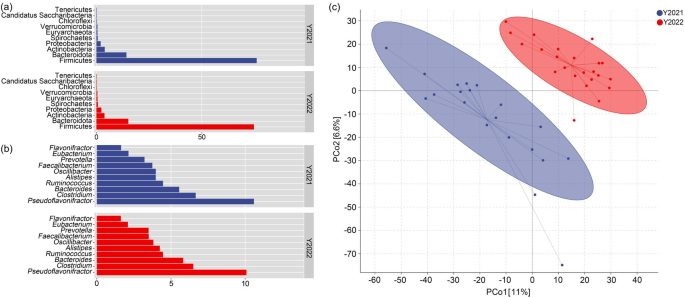
The researchers collected faecal and snow urine samples from wild red deer in the Gaogesitai National Nature Reserve over two consecutive winters. They measured the levels of faecal nitrogen (FN) and the ratio of urea nitrogen to creatinine (UN:C) in the samples, which are established indicators of an animal’s nutritional status. The results showed that the FN levels were significantly lower and the UN:C ratios were higher in the winter of 2022 compared to 2021, suggesting that the red deer faced greater nutritional stress in the more recent winter.

Gut Microbiome Responds to Nutritional Challenges
To further investigate the link between gut microbes and nutritional status, the researchers conducted nutritional control experiments with captive red deer. They simulated the nutritional challenges faced by wild red deer by providing them with low-protein, low-energy diets and limited food resources. The gut microbiome of the captive deer showed similar changes to those observed in the wild red deer, with increases in the abundances of Ructibacterium, Butyrivibrio, and decreases in Acetatifactor and Cuneatibacter.

Functional Changes in the Gut Microbiome
The researchers also examined changes in the functional capabilities of the gut microbiome. They found that during periods of nutritional stress, the gut microbes exhibited increased activity in pathways related to cell growth and death, while pathways involved in lipid metabolism, particularly the synthesis of secondary bile acids, were significantly reduced. These functional shifts mirror the physiological changes observed in the wild red deer, suggesting that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in the animals’ adaptation to nutritional challenges.
Implications for Wildlife Conservation
The findings of this study highlight the importance of monitoring the gut microbiome as a non-invasive tool for assessing the nutritional health of wild ungulate populations. By identifying key microbial indicators of nutritional stress, such as the changes in Ructibacterium, Butyrivibrio, Acetatifactor, and Cuneatibacter, as well as shifts in functional pathways related to cell growth and lipid metabolism, wildlife managers can gain valuable insights into the well-being of red deer and other wild ungulates.

Adapting to a Changing World
As climate change and other environmental pressures continue to impact the habitats of wild ungulates, understanding how these animals adapt to nutritional stress will be crucial for their long-term conservation. This study provides a foundation for further research into the complex relationship between gut microbes, nutritional status, and the overall health of wild ungulate populations. By unraveling these intricate connections, scientists and conservationists can work towards more effective strategies to protect and sustain these vital components of forest ecosystems.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Jinhao Guo, Zheng Li, Xinxin Liu, Yongchao Jin, Yue Sun, Ziao Yuan, Weiqi Zhang, Jialong Wang, Minghai Zhang.
For More Related Articles Click Here
