A Florida startup, Star Catcher, has successfully demonstrated its wireless energy-beaming technology by transmitting solar power across the full length of an NFL football field. This milestone brings us one step closer to space-based solar power and unlocking new capabilities for satellites and space exploration. The company plans to launch a network of energy-beaming satellites in low Earth orbit to provide power to both ground and space-based receivers.
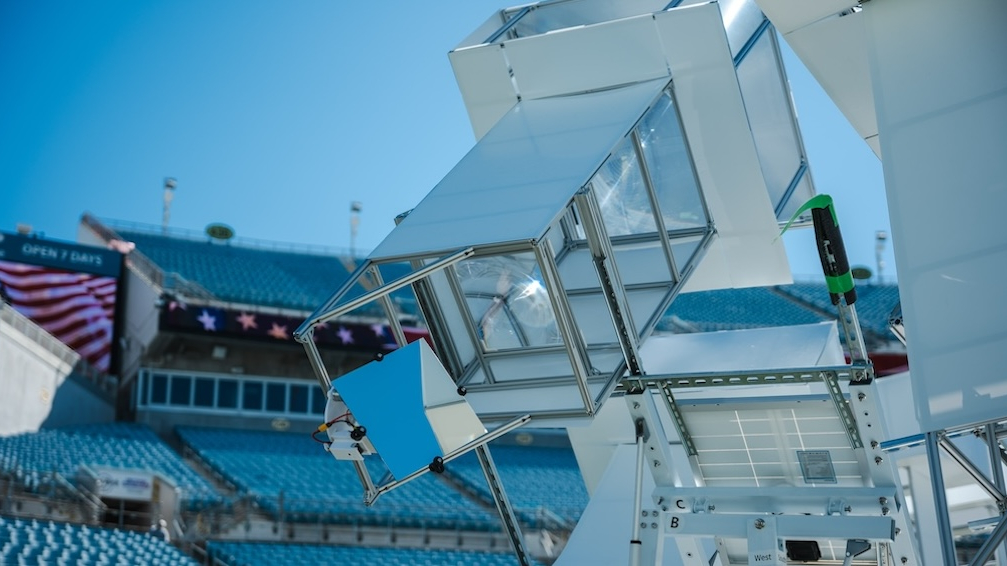
Star Catcher’s Groundbreaking Wireless Energy Transmission Demonstration
In a remarkable feat, Star Catcher, a Florida-based startup, has successfully completed a ground demonstration of its wireless energy-beaming technology. The test, which took place at EverBank Stadium, home of the NFL’s Jacksonville Jaguars, proved the company’s ability to collect solar power and wirelessly transmit it across the full 300-foot (90-meter) length of the football field.
This demonstration marks a significant milestone in the development of orbital systems capable of collecting energy from the sun and wirelessly transferring it to ground or space-based receivers as usable electricity. According to Andrew Rush, the Co-Founder and CEO of Star Catcher, “This demonstration marks the first end-to-end test of our space power beaming technology, proving we can collect and wirelessly transmit energy with the precision needed for space applications.”
The electricity was beamed to multiple solar array receivers, which were built using already available components to ensure backward-compatibility with existing satellite power systems. This successful test puts Star Catcher one step closer to realizing its goal of eliminating power constraints in space and unlocking new capabilities for satellites and the customers they serve.
Powering the Future: Star Catcher’s Plans for a Space-Based Energy Grid
Star Catcher’s ultimate goal is to operate a constellation of satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO) that are capable of providing a continuous supply of power to ground receivers, satellites, spacecraft, and even space stations. The company’s recent success follows a $12.25 million boost in seed funding from Initialized Capital and B Capital, which has allowed them to accelerate their development efforts.
After the successful demonstration at EverBank Stadium, Star Catcher plans to conduct a much larger-scale test this summer at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. During this test, the company aims to beam hundreds of watts of electricity nearly a mile (over half a kilometer) across the runway once used to land the agency’s space shuttles, while simultaneously powering several mock satellites.
If these larger-scale tests prove successful, Star Catcher hopes to begin launching its “Star Catcher Network” of energy-beaming satellites to LEO as early as the end of 2025. This network is designed to provide energy to customers both on Earth and in orbit, potentially revolutionizing the way we power our space-based operations and infrastructure.
The development of space-based solar power systems, like those being pioneered by Star Catcher, could have far-reaching implications for the future of energy and space exploration. By harnessing the abundant and consistent solar energy available in space, these systems could potentially provide a reliable and sustainable source of power for a wide range of applications, from powering satellites and space stations to beaming energy back to Earth.
The Potential Impact of Star Catcher’s Technology on the Future of Energy and Space Exploration
The successful demonstration of Star Catcher’s wireless energy-beaming technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our space-based operations and infrastructure. By creating a network of energy-beaming satellites in low Earth orbit, the company aims to provide a reliable and sustainable source of power for a wide range of applications, from powering satellites and space stations to beaming energy back to Earth.
This technology could have far-reaching implications for the future of energy and space exploration. By harnessing the abundant and consistent solar energy available in space, space-based solar power systems could potentially eliminate the power constraints that have long plagued space-based operations, unlocking new capabilities for satellites and the customers they serve.
Moreover, the ability to wirelessly transmit energy from space to ground-based receivers could also have applications on Earth, potentially providing a clean and renewable source of power to communities around the world. As the global demand for energy continues to grow, and the need to transition away from fossil fuels becomes increasingly urgent, technologies like those being developed by Star Catcher could play a crucial role in shaping the future of our energy landscape.
