Researchers at Tufts University have taken inspiration from the beloved superhero Spider-Man and created the first real-life web-slinging technology. This innovative breakthrough allows a fluid material to shoot from a needle, instantly solidify into a string, and adhere to and lift objects. The researchers have leveraged the power of silk fibroin, a natural material found in silk moth cocoons, to develop this bio-inspired technology. This remarkable advancement showcases how scientific imagination, combined with engineering prowess, can transform fictional ideas into tangible reality.
Unlocking the Secrets of Spider-Silk Technology
Every child who has ever read a comic book or watched a Spider-Man movie has dreamed of the incredible web-slinging abilities of the iconic superhero. Researchers at Tufts University took this childhood fantasy seriously and set out to recreate the web-slinging technology that has captivated audiences for decades.
The key to their success lies in the remarkable properties of silk fibroin, the building block protein found in silk moth cocoons. By boiling these cocoons in a solution and breaking down the fibroin, the researchers were able to create a silk fibroin solution that could be extruded through narrow needles to form a stream. With the right additives, this stream immediately solidifies into a fiber when exposed to air, mimicking the natural process of silk production in nature.
Overcoming Challenges and Unlocking the Power of Silk
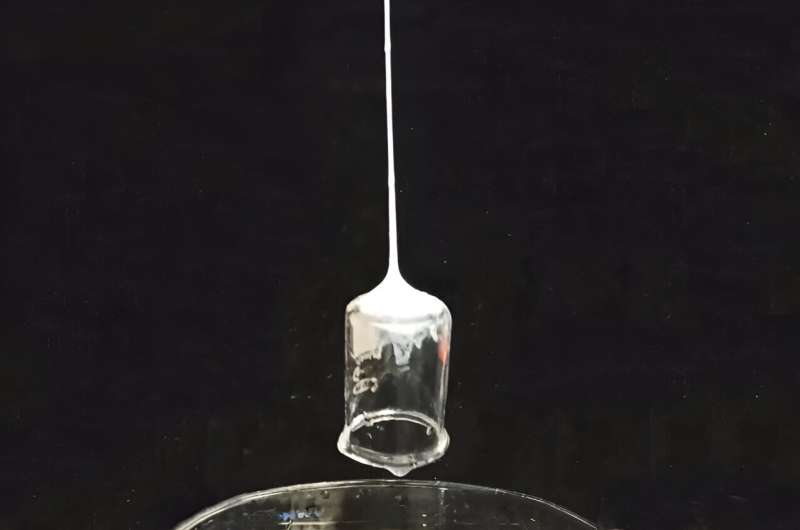
While the researchers made significant progress with silk-based materials, they faced a significant challenge in replicating the mastery of spiders, which can control the stiffness, elasticity, and adhesive properties of their threads. The breakthrough came about purely by accident, as one of the researchers discovered a web-like material forming on the bottom of a glass while cleaning with acetone.
This accidental discovery helped the team overcome several engineering hurdles. The addition of dopamine, a compound used in making adhesives, allowed the solidification process to occur almost instantly. By combining the silk fibroin solution with dopamine and other additives like chitosan and borate buffer, the researchers were able to create fibers with exceptional tensile strength and adhesiveness, capable of lifting objects over 80 times their own weight.
Bringing Comic Book Dreams to Life: The Future of Spider-Man-Inspired Technology
While natural spider silk remains about 1,000 times stronger than the man-made fibers developed in this study, the researchers are confident that with continued innovation and engineering, their technology will continue to improve and pave the way for a variety of technological applications.
As Fiorenzo Omenetto, the director of the Silklab at Tufts University, aptly stated, “As scientists and engineers, we navigate the boundary between imagination and practice. That’s where all the magic happens.” The team’s ability to be inspired by nature, comics, and science fiction has enabled them to reverse-engineer their silk material to behave in ways that mimic the original design of nature and the imaginative creations of comic book writers. With this groundbreaking work, the researchers have taken a significant step towards turning the fantastical web-slinging abilities of Spider-Man into a tangible reality.
