Researchers have discovered that the process of mRNA translation and decay is tightly coupled, with the ribosome, SKI complex, and exosome forming a supercomplex to efficiently manage this critical cellular function. This finding provides new insights into the mechanistic interactions of these key protein complexes and offers a better understanding of the cellular quality control machinery.
Uncovering the Supercomplex of mRNA Metabolism
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the crucial blueprint for protein production within cells. When an mRNA molecule is no longer needed, it must be efficiently degraded to maintain cellular homeostasis. Researchers led by Elena Conti at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry have made a groundbreaking discovery, revealing that the key molecular machines involved in mRNA translation and decay are physically linked, forming a supercomplex.
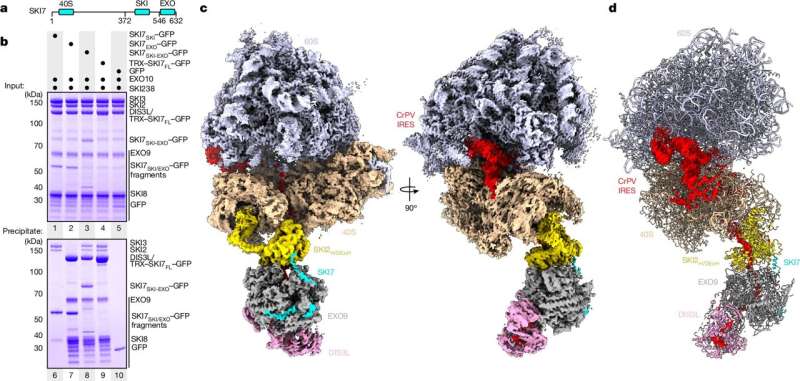
This supercomplex consists of the ribosome, the SKI complex, and the exosome. The ribosome is the cellular ‘protein factory,’ translating mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids. The SKI complex then targets the mRNA for degradation by the exosome, which functions as a molecular ‘shredder.’ By showing that these three complexes assemble into a single supercomplex, the researchers have uncovered a previously unknown level of coordination in the regulation of mRNA metabolism.
Deciphering the Structural Basis of the Supercomplex
To understand the structural details of this supercomplex, the researchers employed cutting-edge techniques, including cryo-electron microscopy and the AI-powered protein structure prediction tool AlphaFold. These advancements have enabled scientists to examine much larger protein machines and elucidate how they interact.
The high-resolution structural data revealed that the individual protein complexes are in close physical contact, similar to the components of a quality control unit in an industrial production line. The SKI complex is able to attach itself to the ribosome when an error in the mRNA is detected, unwind the mRNA into a linear strand, and then transfer it to the exosome for degradation. This process is facilitated by the protein SKI7, which bridges the interaction between the SKI complex and the exosome.
Connecting Translation and Decay: The Significance of the Supercomplex
The discovery of the mRNA translation and decay supercomplex has significant implications for our understanding of cellular quality control mechanisms. By physically linking the processes of mRNA translation and degradation, the cell can efficiently coordinate these crucial functions and ensure the timely removal of mRNAs that are no longer needed or defective.
This finding also sheds light on the specific scenarios in which the supercomplex comes into play. For instance, when two ribosomes collide while translating a damaged mRNA, the SKI complex is recruited to target the mRNA for degradation by the exosome. The supercomplex, therefore, acts as a vigilant quality control system, swiftly identifying and eliminating problematic mRNAs to maintain cellular homeostasis and optimize protein production.
