Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery about Jupiter’s iconic Great Red Spot (GRS), revealing unexpected size changes and complex behavior. Using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, scientists have assembled a time-lapse movie showcasing the squiggly, jiggling motion of this massive anticyclone, which is large enough to swallow the Earth. This new insight into the dynamics of the solar system’s largest storm provides a broader cosmic context for understanding the meteorology of planets around other stars. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and Hubble Space Telescope are the key topics explored in this blog post.
The oscillating nature of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot deduced by researchers
The great red spot of Jupiter is the oldest storm to have been observed, a massive anticyclone that could swallow our entire planet and has been studied for more than 150 years. But new observation from the Hubble Space Telescope has revealed an unexpected revelation.
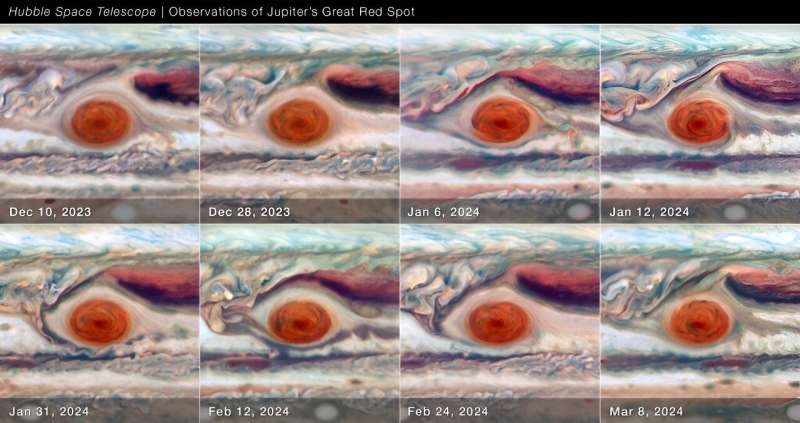
The GRS, it turns out, is not as stable as we thought; over the span of just a few decades (a drop in the bucket compared to the planet’s lengthy history), the entire storm has decreased in area. The Hubble data was gathered over 90 days spanning December 2023 to March 2024, and it depicts the GRS “waggling back and forth as if it were a bowl of Jell-O. As it sped around Jupiter, the storm quickly grew and shrank in size with its length dominating width of Texas at times while other times the fast winds stretched across nearly Jupiter’s diameter.
Although we knew the longitude changes a little over time, seeing the size spin backwards was completely unexpected!! As far as we know, it’s never been seen before,” said Amy Simon of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, who led the study.
Revealing the complex nature of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
The Hubble observations reveal high-altitude oval-shaped features within the Great Red Spot that were not present during previous studies. The telescope’s high-res imaging capabilities allowed the researchers to get really close looks at not just the size and shape of the storm, but also its extremely subtle color shifts.
A lot of things are moving from day-to-day,” Simon said. The team found that the unusual core of the storm brightens when the GRS is at its largest, implying that there is less haze in the upper atmosphere.
Whether the two lobes of material surrounding GRS are connected or disconnected at depth below that, nobody knows,” said co-investigator Mike Wong of the University of California at Berkeley, “This is a challenge to our current understanding–nobody really understands how this phenomenon is happening. This seesaw with the jets is what causes the GRS to wobble back and forth.
What it means for planetary meteorology
The research on the Great Red Spot of Jupiter and its puzzling size fluctuations offer significant information to understand the meteorology of exoplanets.
“Learning how the major storms in our solar system work helps us tease out the physics of how hurricanes form on Earth; they’re part of a larger cosmic continuum,” Simon added.
The researchers are looking forward to additional, high-resolution observations from Hubble and other more advanced telescopes which could find more parameters on Jupiter that impact the GRS oscillation. Find out how disentangling the intricate workings of this iconic storm can help planetary scientists develop a better understanding of atmospheres across the diverse worlds that exist throughout our Universe.
