Dental implants have become a popular solution for missing teeth, but their cement-retained restorations can pose a serious threat – excessive cement residue under the gingiva can lead to peri-implant diseases and even implant loss. This new study explores the factors that influence the amount of remnant cement in the subgingival region, providing valuable insights for dentists to minimize this risk. The findings suggest that slower crown seating speed, smaller cement quantity, and gentler seating force can significantly reduce the leftover cement, while the type of cement used also plays a crucial role. Understanding these factors can help dental professionals deliver safer and more successful implant restorations. Dental implants and peri-implant diseases are important topics in the field of dentistry.
The Challenge of Cement Residue in Implant Restorations
Dental implants have revolutionized the way we replace missing teeth, offering a stable and long-lasting solution. However, the cement-retained implant crowns, where the restoration is cemented onto the implant abutment, can pose a significant challenge. The leftover cement that seeps into the delicate gingival (gum) area around the implant can lead to a host of problems, including peri-implant diseases and even implant loss.
Investigating the Factors that Influence Remnant Cement
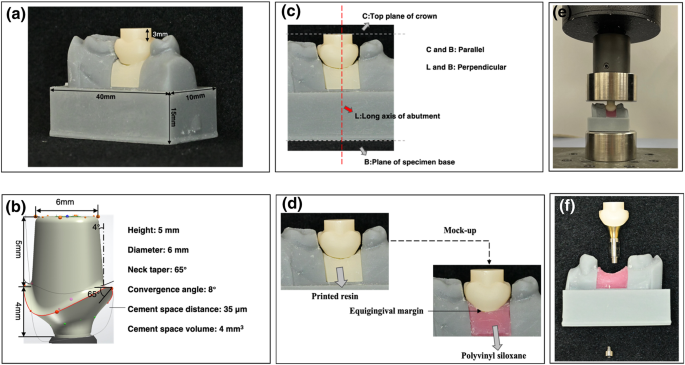
In this study, researchers set out to evaluate the effects of various crown seating methods on the amount of remnant cement in the subgingival (below the gum) region. They examined the impact of crown seating speed, seating force, quantity of cement used, and the type of cement on the remnant cement.
Slower is Better: Crown Seating Speed and Force
The results showed that as the crown seating speed and force increased, the amount of remnant cement also increased significantly. This is due to the shear-thinning properties of the cement, which cause it to flow more rapidly when the crown is seated quickly or with greater force. Therefore, the researchers recommend using a slower, more controlled crown seating process to minimize the cement residue.
Quantity Matters: Cement Usage
The study also found that using a smaller quantity of cement resulted in less remnant cement in the subgingival region. This is because any excess cement beyond the cement lute space (the space between the crown and abutment) will be extruded into the gingival area. By carefully calculating the appropriate amount of cement based on the restoration’s cement space, dentists can reduce the risk of cement overflow.
Cement Type Plays a Role
The type of cement used also had a significant impact on the remnant cement. The cement with the highest flowability, zinc oxide noneugenol cement (TBN), had the highest remnant cement values, while the methacrylate cement (ME) had the lowest. This suggests that cements with lower viscosity and higher flowability are more prone to spreading into the subgingival region.
Implications for Safer Implant Restorations
The findings of this study provide valuable guidance for dental professionals in delivering safer and more successful implant restorations. By controlling the crown seating speed and force, using the minimum required amount of cement, and selecting the appropriate cement type, dentists can significantly reduce the risk of cement residue and the associated peri-implant diseases. This knowledge can help improve the long-term success of cement-retained implant prostheses and ensure better outcomes for patients.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Fanghui Ji, Ji Suk Shim, Jeongyol Lee, Hwiseong Oh, Jae Jun Ryu.
For More Related Articles Click Here
