Researchers have found that a single dose of a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor can significantly improve the cognitive functions of aged mice, offering hope for addressing age-related memory decline. The study revealed that this treatment not only enhances spatial memory in older mice but also affects the concentrations of various metabolites in different brain regions. These findings suggest a complex interplay between cellular metabolism and neuroplasticity, which could be a promising target for developing anti-aging therapies. Memory and cognitive function are crucial for maintaining a high quality of life as we age, and this research provides valuable insights into potential strategies for preserving brain health.
Unlocking the Secrets of Aging Brains
As we grow older, our cognitive abilities can gradually decline, making it harder to remember important information or navigate our surroundings. This age-related memory loss is a common challenge faced by many individuals, and understanding the underlying mechanisms is a crucial goal for researchers in the field of neuroscience.
In a recent study, a team of scientists from Poland have made an intriguing discovery: a single dose of a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor can significantly improve the cognitive functions of aged mice. Glycogen phosphorylase is an enzyme that plays a key role in the breakdown of glycogen, a critical energy storage molecule in the brain. By inhibiting this enzyme, the researchers were able to observe remarkable changes in the way the older mice’s brains processed information.
Boosting Spatial Memory in Aged Mice
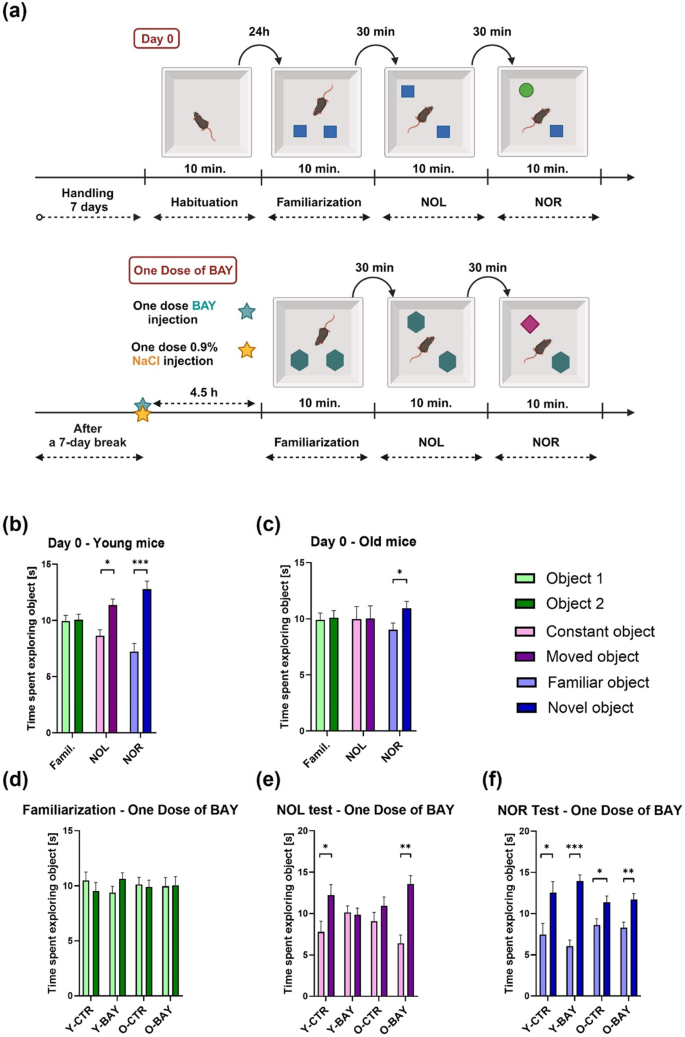
The researchers conducted a series of behavioral tests to assess the cognitive abilities of young and old mice, both before and after the administration of the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor. In the Novel Object Location (NOL) test, which measures spatial memory, the older control mice showed no preference for exploring the object that had been moved to a new location, suggesting impaired spatial memory. However, when the aged mice were given a single dose of the inhibitor, they exhibited a significant improvement in their ability to recognize the object in its new position.
These findings were in contrast to the young mice, which showed the opposite response: their spatial memory was impaired after receiving the inhibitor. This divergent effect highlights the complex interplay between cellular metabolism and neuroplasticity, and suggests that the aging brain may respond differently to the modulation of glycogen metabolism compared to its younger counterpart.
Metabolic Shifts in the Aging Brain
To further explore the underlying mechanisms, the researchers conducted a comprehensive metabolomic analysis of the mice’s brains. They examined the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum – three key brain regions involved in memory formation and cognitive function.
The analysis revealed that aging led to a reduction in the levels of numerous metabolites across these brain regions, particularly in the hippocampus and cerebellum. Interestingly, the administration of the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor in aged mice was able to “rejuvenate” the levels of several metabolites, including those involved in energy production, signaling, and lipid metabolism.
A Promising Approach to Combating Age-Related Memory Decline
These findings suggest that the inhibition of glycogen breakdown can have a profound impact on the metabolic landscape of the aging brain, potentially unlocking new avenues for therapeutic intervention. By targeting the complex interplay between cellular metabolism and neuroplasticity, this approach holds promise for developing strategies to combat age-related memory decline and maintain cognitive function as we grow older.
The researchers emphasize that the observed effects of a single dose of the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor were long-lasting, lasting for at least 5 hours. This indicates that this relatively simple intervention could potentially lead to enduring improvements in cognitive performance, without the need for continuous or prolonged treatment.
Unlocking the Mysteries of the Aging Brain
As with any scientific discovery, this research raises new questions and opens up exciting possibilities for further exploration. Understanding the precise mechanisms by which glycogen metabolism influences neuronal function and synaptic plasticity in the aging brain is a critical next step. Additionally, exploring the potential applications of this approach in the context of age-related neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, could lead to groundbreaking advancements in the field of brain health.
By shedding light on the complex interplay between cellular metabolism and cognitive function, this study serves as a valuable contribution to our understanding of the aging brain. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this remarkable organ, the potential to develop effective interventions that can preserve memory and cognitive abilities well into our golden years grows ever brighter.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Natalia Pudełko-Malik, Dominika Drulis-Fajdasz, Łukasz Pruss, Karolina Anna Mielko-Niziałek, Dariusz Rakus, Agnieszka Gizak, Piotr Młynarz.
For More Related Articles Click Here
