A groundbreaking study reveals that closely related plant populations can employ vastly different strategies to adapt to the same environmental stressor, challenging the common assumption that such species adapt in uniform ways. This discovery holds exciting implications for engineering climate-resilient crops to address future food security challenges.
Flexibility in EvolutionDefying expectations
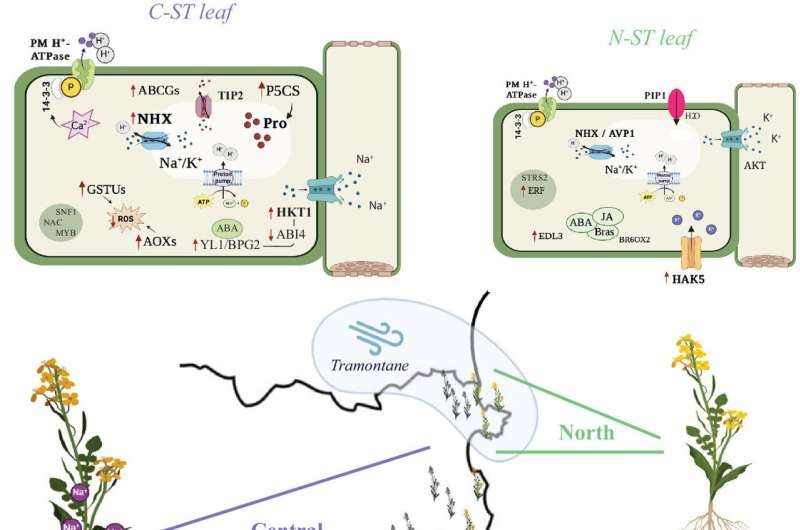
Contrary to the popular belief that directly related populations of a species would adapt to an environmental stressor in much the equivalent way, Botanists at the University of Nottingham have revealed a degree of ‘evolutionary flexibility’ in the species Brassica fruticulosa.
This species is closely related to many important crop plants such as cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, rapeseed, and radish so it exhibits needs arising from both an aggressive colonizing ability in disturbed areas and a seed dispersal strategy. Through a detailed survey of the Brassica species in the coastal regions of Northern Spain, an isolated example was recognized among all other F2 populations and it showed strong adaptation to high salinity, which was probably not found in the remaining F1 population from the same sea beet plant.
The researchers went on to uncover the alternative mechanisms through genomics, physiology, and molecular biology that these neighboring populations of Brassica fruticulosa had evolved to address the top selective pressure on any habitat — high salinity. The blind salamander finding defies this basic assumption that species with closely related genomes should be genetically or physiologically constrained in their capacity for parallel change.
Unmasking the Secrets of Adaptation
Professor Levi Yant from the School of Life Sciences at The University of Nottingham led the research team and said: “We were amazed to find that the different populations derived from clearly separated and distinct clades within Brassica fruticulosa, had each adapted differently, even in opposite directions, for coping with salinity along high-salinity coastal environments.
People generally think that closely related populations of a given species should all adapt in the same way to the same environmental challenge, given fundamental genetic or physiological constraints,” said lead author Professor Laurel Symes. ‘What hasn’t been widely tested, however, had been finding itself to be quite impractical.
For the study, Dr. Silvia Busoms decided to compare many populations rather than just a few to have a broader view of the adaptation strategies within this species.
‘In our current study we demonstrate that even at the scale of neighboring populations distinct modes of selection underlie localized adaptive responses to high coastal salinity in Brassica fruticulosa,’ noted Professor Yant. This suggests many choices for genetic tinkering in a key agricultural trait: soil salinity.
Conclusion
This finding raises important implications for agriculture; it suggests that related plants appearing similar on the outside may employ very different methods of adapting to specific environmental conditions and that such nuances are critical as we seek to feed a growing global population. With insight into the various types of adaptation mechanisms within a single species, researchers may be able to discover ways to produce more climate-resistant crops that can survive under difficult conditions such as soil salinization, among other environmental stresses. Using this information could be a crucial tool in fighting climate change, its odd effects, and feeding the world.
