Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental condition that affects millions of children worldwide. ADHD is characterized by difficulties in maintaining focus, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, which can significantly impact a child’s academic and social success. Researchers have now developed a groundbreaking deep learning-based method that can accurately classify ADHD subtypes and distinguish children with ADHD from their typically developing peers by analyzing the dynamic patterns of brain activity. This innovative approach holds immense potential as an effective diagnostic tool, enabling timely interventions and improving the lives of those affected by this complex disorder.
Unraveling the Complexities of ADHD
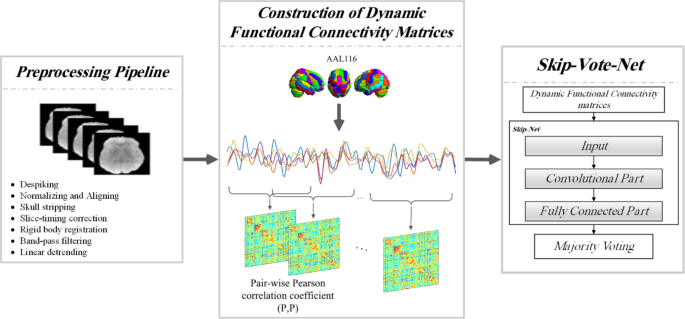
ADHD is a prevalent mental disorder that affects an estimated 8-11% of school-age children, and up to 50% of these individuals continue to experience ADHD symptoms into adulthood. Children with ADHD often struggle to maintain focus on tasks, leading to challenges in academic achievement, social interactions, and professional development. Traditionally, the diagnosis of ADHD has relied on the subjective observations of clinicians, which can be prone to biases and delays in treatment initiation.
Harnessing the Power of Brain Imaging and Machine Learning
To address these challenges, researchers have turned to advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as Click Here
