Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a groundbreaking new copper metal-organic framework (MOF) nanozyme that is set to transform the world of food detection. These nanozymes, with their high catalytic activity, stability, and adaptability, are poised to become the next-generation sensitive materials for building cutting-edge sensors. Nanozymes have long been a focus of intense research, and this new development promises to take the field to new heights. By leveraging the unique properties of these nanomaterials, the team has created an intelligent food detection system that is both sensitive and rapid, capable of identifying and quantifying a range of bioactive substances in food samples.
Transforming Food Detection with Smart Nanozymes
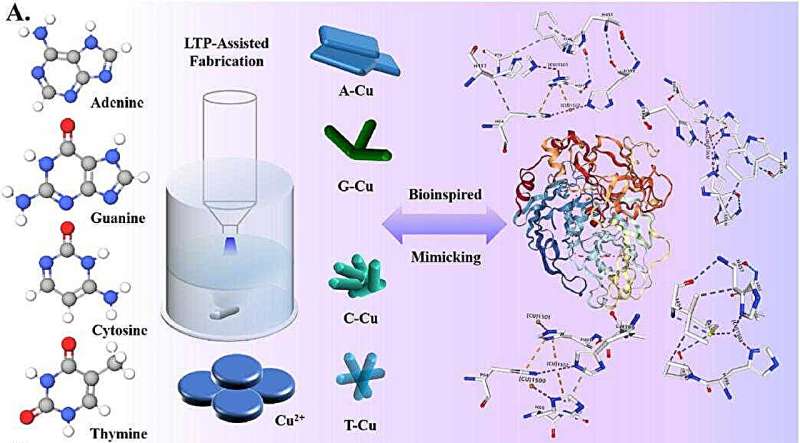
This breakthrough is achieved by using the unique gas-liquid interface dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) low-temperature plasma (LTP) technology of the research group to prepare copper metal-organic framework nanoparticlezymescascade. The nanozymes, which resemble the actions of a laccase enzyme in nature, respond differently to five well-known bioactive molecules within food.
The high-throughput, sensitive and rapid detection with quantitative analysis can be extended to the concentration range of 1.5–150 μg/mL by fabrication of an encoded array sensor for all these substances using even lower majority at concentrations close to their recommended therapeutic levels (versatile). These sensors will be used for intelligent sensing and identification of bioactive components in food according to the study, which was published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics, that will change our approach to food safety and quality.
The potential of smartphone-enabled food inspection
A user gets excited about this new technology as it is of more use and portability. This colorimetric change caused by the nanozymes can be detected by various electronic tools, such as smartphones, so that nanosensors would show promise when carried out on-the-go for food inspection and analysis.
This integration makes food detection more ultra-widely accessible than ever before, and opens up the possibility for intelligent rapid food detections with higher convenience. Through utilizing the widespread adoption of smartphones, researchers have designed a system that can be available for consumers, food producers and regulatory agencies — establishing an all-encompassing and efficient food safety landscape.
This simple and highly sensitive detection technology manifests an epoch-making contribution to the food industry. It is also groundbreaking and could change forever how we think about risks in food safety, giving everyone from individual consumers to large organizations new information which they can use to decide what food to eat or deliver.
Novel Dimension of Preparation and Application of Nanozymes
Aside from the food detection application of copper MOF nanozymes, this study suggest a thorough roadmap for such an active and stable nanozyme preparation. This gas–liquid interface DBD LTP technology was applied to manufacture the wide variety of nanozymes using various base ligands, which have their distinctive properties for its applications.
Such versatility of these nanozymes holds great potential on its application in food detection and other fields as well which include environmental monitoring, disease diagnosis and therapeutic development.
This work not only provides a new synthesis way of high-efficiency nanozymes but also develops an intelligent and convenient strategy for food detection, as the researchers point out. This research opens up a whole new series of commercial solutions for consumers and developers, thanks to being able to both do it fast and cheap with the cutting-edge of nanomaterial science in everyday practical applications.
