A team of researchers from Vanderbilt University have released a groundbreaking benchmarking study that aims to assist scientists in navigating the complex world of spatial transcriptomics. This study, led by Dr. Xin Maizie Zhou, evaluates various computational tools used in spatial transcriptomics, a technology that maps gene expression patterns in tissues while preserving their spatial context. The findings of this study offer practical recommendations for researchers working in this rapidly growing field, helping them to identify the most effective methods for their specific research needs.
Nanoseq — Unpacking the Spatial Transcriptome Gradient
IntroductionSpatial transcriptomics is a transformative method that has changed how researchers perceive intricate tissues. The method involves slicing up a tissue sample and depositing it on a specially designed slide with spatially indexed barcodes in order to capture the ribonucleic acid (RNA) in each spot on the tissue. They can then send the RNA through a DNA sequencer, and associate these data with their original locations in the tissue to show which genes were being pumped out where in the architecture of the tissue.
The technology enables many top projects since 2020 and has applications in cancer research, neuroscience etc. Scientists now have the ability to explore regional differentiation of gene expression within the brain, and investigate genes that might work in concert depending on their disease associations or regional localization, suggesting new lines of scientific inquiry.
An Overview of the Spatial Transcriptomics Analysis Toolbox
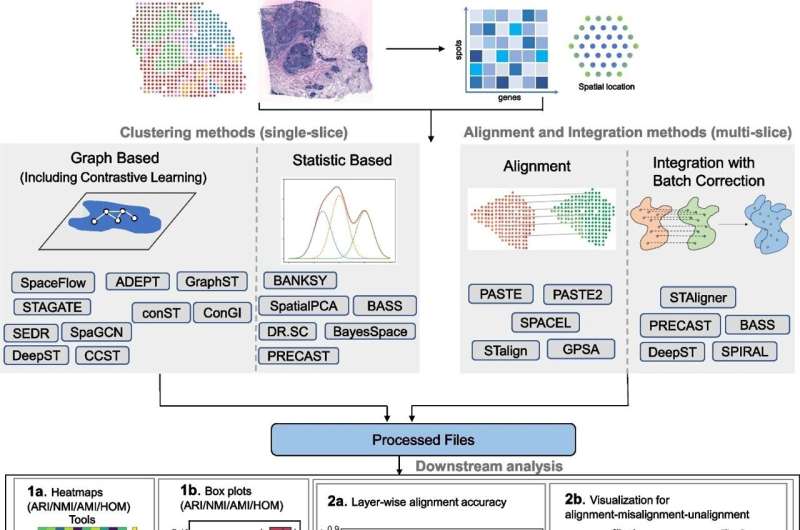
Although spatial transcriptomics is changing fields quite dramatically, the influx of tools can be daunting to… As the Vanderbilt team was aware of this problem, they performed an extensive benchmarking study in order to produce a practical guide for researchers working with cell line data.
The work systematically compared 16 clustering methods, five alignment methods and five integration methods on multiple datasets. The researchers have provided much-needed guidance on selecting the most appropriate methods for specific research questions, based on an impartial evaluation of these computational tools by contrasting their respective strengths and limitations. This study could serve as an essential guide for everyone diving into spatial transcriptomics, thereby supporting precise and reproducible analysis.
Driving the Spatial Transcriptomics Revolution — Empowering Researchers
Results from the Vanderbilt benchmarking study could greatly affect researchers in the spatial transcriptomics field. The researchers have thus allowed scientists to better equip themselves with this very straightforward and handy book for making their choices on which Computational tools to go for in any sort of Analysis.
The first author on the paper, Dr. Xin Maizie Zhou, said; “We set out to create a definitive resource for researchers making their way through the choices that abound in spatial transcriptomics analysis. We are hopeful that this paper will serve as a resource for people within this rapidly evolving field.
Moreover, given the thorough benchmarking results on clustering, alignment and integration strategies provided by this study as well as a set of specific ‘take-home’ messages, this work will doubtlessly become one of the key resources for researchers interested in decoding spatial patterns within tissues to uncover new insights into complex biological processes and diseases.
