A team of researchers at Vanderbilt University has released a new benchmarking study that aims to assist scientists in selecting the most effective methods for analyzing spatial transcriptomics (ST) data. This revolutionary technology allows researchers to map gene expression patterns in tissues while preserving their spatial context, revolutionizing our understanding of complex tissues. The study, led by Xin Maizie Zhou, evaluates computational tools in ST and offers practical recommendations for researchers working in this rapidly growing field. With applications in cancer research and neuroscience, this benchmark study promises to be a valuable resource for anyone exploring the spatial complexities of gene expression.
Navigating the Spatial Transcriptomics Landscape
The advent of spatial transcriptomics (ST) has revolutionized our understanding of complex tissues, opening up new frontiers in cancer research and neuroscience. By mapping gene expression patterns while preserving spatial context, ST has provided unprecedented insights into the intricate workings of the human body.
However, as with any groundbreaking technology, the proliferation of computational tools for analyzing ST data has created a conundrum for researchers. With a variety of clustering, alignment, and integration methods available, it can be challenging to identify the most effective approach for specific research needs. That’s where the Vanderbilt team’s benchmarking study comes into play.
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Spatial Transcriptomics Analysis Tools
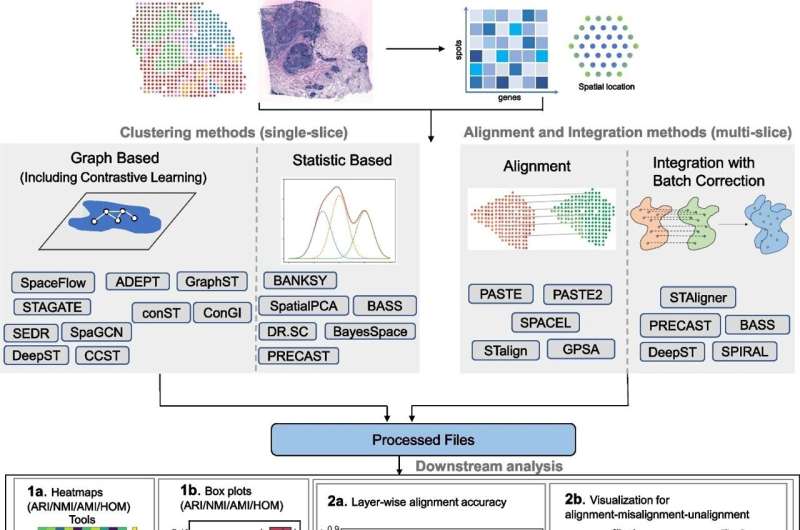
Led by Xin Maizie Zhou, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and computer science, the Vanderbilt team systematically compared 16 clustering methods, five alignment methods, and five integration methods across a diverse range of ST datasets. By thoroughly evaluating the performance of these computational tools, the researchers have provided a clear and accessible guide for navigating the spatial transcriptomics analysis landscape.
The study, recently published in Genome Biology, offers practical recommendations for researchers, helping them identify the tools that best match their specific research requirements. This comprehensive evaluation is particularly valuable in a field where the abundance of options can be overwhelming, making it difficult to choose the most appropriate approach.
Unlocking the Potential of Spatial Transcriptomics
The widespread adoption of spatial transcriptomics since 2020 has been a game-changer in fields like cancer research and neuroscience. By capturing the RNA in specific locations of a tissue sample and mapping it back to the original architecture, ST allows researchers to visualize where certain genes are being expressed within the tissue.
This groundbreaking technology has the potential to unlock new insights into the complex mechanisms underlying disease processes and regional brain functions. However, the effective analysis of ST data is crucial to realizing this potential. The Vanderbilt team’s benchmarking study aims to provide a clear and accessible guide for researchers, empowering them to make informed decisions and select the most appropriate tools for their spatial transcriptomics research. With this valuable resource, the scientific community can continue to push the boundaries of our understanding of the human body and pave the way for innovative breakthroughs.
