The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on mental health, leading to a surge in depression and anxiety worldwide. In this study, researchers from Norway and India explored the complex relationships between lifestyle factors, demographic characteristics, and depressive symptoms among individuals in Kolkata, India during the pandemic. Using an extensive online survey, advanced statistical analysis, and machine learning techniques, the team identified key factors associated with self-reported depression, such as employment status, physical activity, sleep patterns, and dietary habits. The researchers also developed an ontology model to semantically represent the acquired knowledge, providing valuable insights for addressing mental health challenges in the face of challenging societal and environmental conditions. This research offers a data-driven approach to understanding the multifaceted nature of depression and its prevention during the COVID-19 crisis. Depression, COVID-19 pandemic, and lifestyle factors are key topics covered in this study.
Exploring the Impact of Lifestyle and Demographics on Depression During COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted mental health, with a 25% increase in the global prevalence of anxiety and depression reported by the World Health Organization. In India, recent studies have highlighted a significant surge in the prevalence of depression and anxiety among the population amidst the ongoing pandemic. Understanding the complex interplay between lifestyle factors, demographic characteristics, and depressive symptoms during this challenging time is crucial for developing effective interventions and strategies to support mental health.
Uncovering the Connections Through an Online Survey
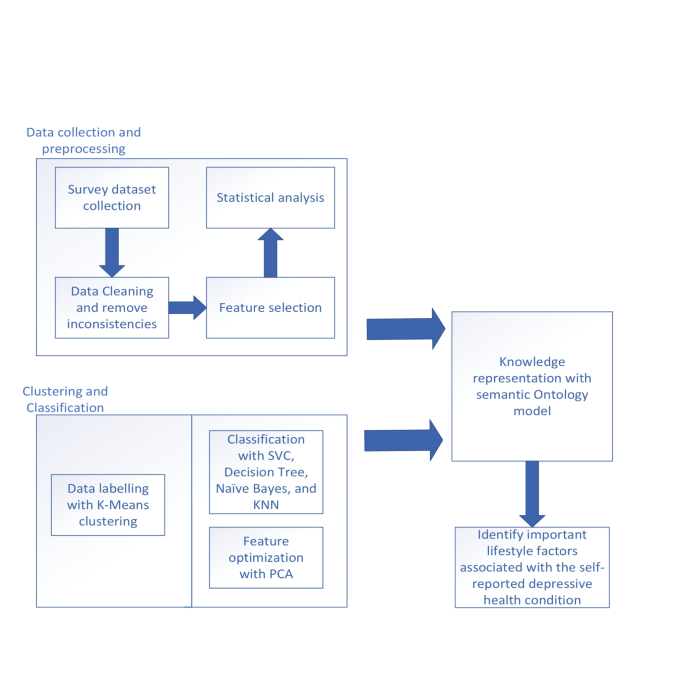
To explore these relationships, researchers from Norway and India conducted an extensive online survey in Kolkata, India, gathering data from over 1,800 participants during the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey focused on capturing information related to personal, behavioral, lifestyle, habitual, and social aspects of the respondents’ lives.
Statistical Analysis and Machine Learning Techniques
The researchers employed a comprehensive analytical approach, utilizing statistical methods and machine learning algorithms to identify the key factors associated with self-reported depressive symptoms. Principal component analysis (PCA) and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used for feature selection, while K-means clustering divided the dataset into five distinct classes. A support vector machine (SVM) classifier with a linear kernel achieved an impressive 96% accuracy in classifying the dataset, and the Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) algorithm provided insights into the model’s decision-making process.
Semantic Representation of Findings
To further enhance the understanding of the acquired knowledge, the researchers developed an OWL (Web Ontology Language) ontology. This semantic model facilitated the representation and reasoning of the survey data, enabling queries and inferences that could aid in the comprehension and mitigation of depression risk factors.
Key Findings and Implications
The study’s findings highlighted a range of factors that significantly influence depressive symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic, including:
– Employment status: Individuals who were unemployed or homemakers exhibited a higher prevalence of depression.
– Physical activity: Engaging in regular physical activity was associated with lower rates of depression.
– Sleep patterns: Disruptions in sleep quality and quantity were linked to increased depressive symptoms.
– Dietary habits: Unhealthy dietary choices, such as reliance on sugary beverages and alcohol, were associated with higher rates of depression.
These insights emphasize the multifaceted nature of depression and underscore the importance of addressing lifestyle and demographic factors in mental health interventions, particularly during challenging times like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Leveraging Online Surveys for Mental Health Research
The study also showcased the advantages of utilizing online surveys for data collection during the pandemic, including cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and the ability to maintain participant anonymity. However, the researchers acknowledged the inherent limitations, such as reaching the target population, addressing language barriers, and mitigating potential biases.
Towards a Comprehensive Understanding of Depression
By combining rigorous statistical analysis, machine learning techniques, and semantic modeling, this research offers a comprehensive approach to understanding the complex relationship between lifestyle, demographics, and depression. The findings provide valuable insights that can inform the development of tailored interventions and support strategies to address the mental health challenges faced by individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Ayan Chatterjee, Michael A. Riegler, Miriam Sinkerud Johnson, Jishnu Das, Nibedita Pahari, Raghavendra Ramachandra, Bikramaditya Ghosh, Arpan Saha, and Ram Bajpai.
For More Related Articles Click Here
