The Gaia space telescope has made a groundbreaking discovery, identifying 55 runaway stars that are careening away from a young star cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud at staggering speeds. This remarkable finding sheds new light on the dynamic evolution of stellar clusters and the critical role of massive stars in shaping cosmic history. Gaia is a European Space Agency mission tasked with mapping the Milky Way in unprecedented detail, providing a unique opportunity to study the movement and properties of stars across our galaxy.
Tracing the Cosmic Escapees
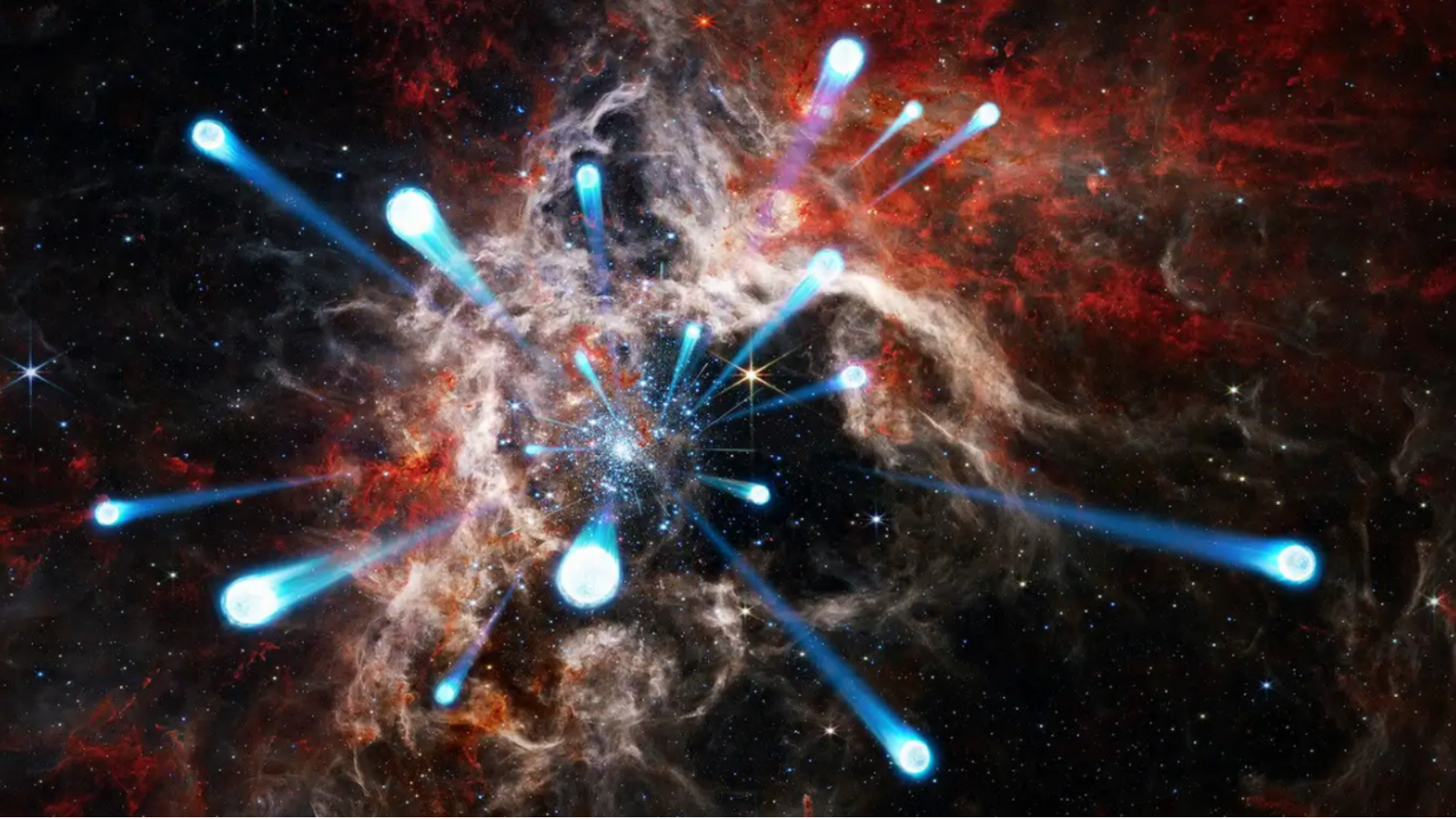
Using the powerful Gaia space telescope, a team of astronomers led by Mitchel Stoop from the University of Amsterdam has made a remarkable discovery: they have identified 55 runaway stars that have been ejected from a young, densely packed star cluster known as R136, located approximately 158,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
This discovery is particularly significant because it represents the first time such a large number of stars have been observed escaping from a single star cluster. The runaway stars are racing away from their birthplace at staggering speeds, some reaching over 62,000 mph (100,000 kph) – roughly 80 times the speed of sound on Earth. These cosmic escapees are massive enough to end their lives in dramatic supernova explosions, leaving behind black holes or neutron stars that will behave like ‘cosmic missiles’ – shooting up to 1,000 light-years from their origin point.
Unraveling the Cluster’s Turbulent History
The researchers discovered that the ejection of these runaway stars occurred in two distinct episodes over the last two million years. The first episode took place around 1.8 million years ago, shortly after the formation of the R136 cluster, with stars being ejected during the cluster’s initial stages of development.
However, the team was surprised to find that a second, more recent episode of stellar escape had occurred just 200,000 years ago. This second event had ‘very different characteristics’ compared to the first, with the runaway stars moving more slowly and in a preferred direction, rather than being shot away in random directions.
The researchers believe that this second episode of stellar ejection was likely the result of an interaction between R136 and another nearby star cluster that was only discovered in 2012. This interaction may have led to the two clusters mixing and merging in the near future, with significant implications for the evolution of this dynamic stellar environment.
The Significance of Runaway Stars and Their Cosmic Impact
The discovery of these 55 runaway stars has far-reaching implications for our understanding of star cluster dynamics and the role of massive stars in shaping the cosmos. The team estimates that R136 may have launched away as many as a third of its most massive stars in the last few million years, with these stellar escapees having a significant impact on their surrounding environment.
Massive stars like those ejected from R136 are known to be millions of times brighter than our Sun, emitting much of their energy as intense ultraviolet light. This powerful radiation can have a profound influence on the structure and evolution of galaxies, potentially even contributing to the ‘re-ionization’ of the early universe – a crucial phase in cosmic history when light from early stars created bubbles of ionized gas in interstellar material.
The team’s findings also highlight the importance of Gaia’s capabilities in mapping the Milky Way and its surroundings in unprecedented detail. By studying the movement and properties of stars in distant galaxies like the Large Magellanic Cloud, researchers can gain valuable insights into the dynamic processes that shape the evolution of stellar clusters and their impact on the larger cosmic landscape.
