Researchers have developed a powerful machine learning model that can accurately predict the risk of needing a pacemaker after a transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) procedure. TAVI is a minimally invasive surgery used to replace a damaged aortic valve, but one of the common complications is the need for a permanent pacemaker. By incorporating detailed data from computed tomography (CT) scans, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and other clinical tests, the new model can forecast these pacemaker needs with up to 92% accuracy. This breakthrough could help doctors better prepare patients and optimize their care before and after TAVI, ultimately reducing complications and improving outcomes. The research highlights the growing potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to transform cardiovascular medicine and deliver more personalized, data-driven care. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation, Pacemaker, Machine learning, Computed tomography
Predicting Pacemaker Needs with Machine Learning
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is a revolutionary procedure that has transformed the treatment of severe aortic stenosis, a debilitating heart condition. By replacing a patient’s damaged aortic valve through a minimally invasive approach, TAVI offers a life-saving alternative for those who are too high-risk for traditional open-heart surgery. However, one of the common complications associated with TAVI is the need for a permanent pacemaker implantation (PMI).
Pacemaker implantation is required in up to 1 in 5 patients after TAVI, as the procedure can disrupt the heart’s natural electrical conduction system. This poses significant risks, including increased hospital stays, infection, and the potential development of heart failure. Identifying patients most likely to require a pacemaker is crucial for optimizing their care before, during, and after the TAVI procedure.
Leveraging Multimodal Data with Machine Learning
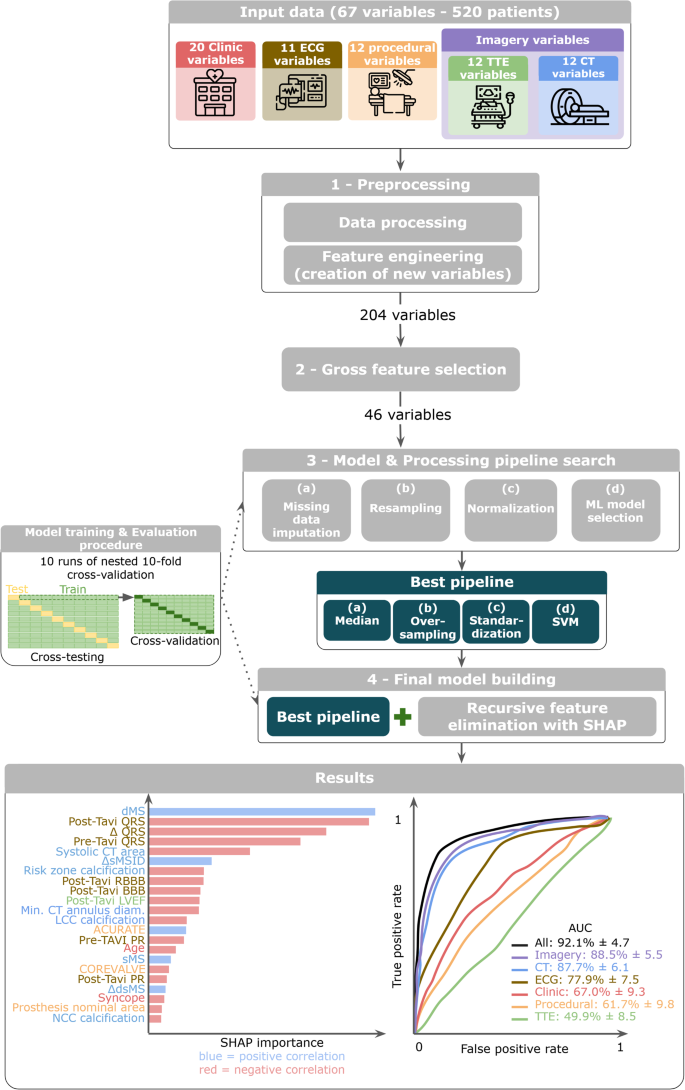
A team of researchers from the University of Brest in France has developed a novel machine learning (ML) model that can accurately predict the risk of PMI following TAVI. Unlike previous approaches that relied primarily on clinical data, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and echocardiography, this new model integrates a wealth of information from computed tomography (CT) scans – a crucial advancement.
The researchers collected data from 520 TAVI patients, including clinical history, ECG readings, transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) results, and detailed CT imaging of the heart and surrounding anatomy. Using advanced ML techniques like Support Vector Machines, the team trained their model to identify the most important predictors of PMI risk.
The Power of CT Imaging Data
A key finding from the study was the critical role of CT imaging data in enhancing the model’s predictive accuracy. While previous models had primarily relied on clinical, electrical, and echocardiographic variables, this new approach demonstrated that incorporating detailed CT measurements – particularly of the membranous interventricular septum – significantly improved the ability to forecast pacemaker needs.
Specifically, the researchers found that the length of the membranous septum, as well as its dynamic changes throughout the cardiac cycle, were among the most influential predictors in the model. This anatomical feature is closely associated with the heart’s electrical conduction system, and its characteristics can indicate the likelihood of conduction disturbances that may require pacemaker implantation.
Towards Personalized, Data-Driven Care
By achieving an impressive 92% accuracy in predicting PMI risk, the researchers have developed a powerful tool that can transform patient management before and after TAVI procedures. Clinicians can now input a patient’s data into the model and receive a personalized risk assessment, enabling them to make more informed decisions about monitoring, pacemaker planning, and post-operative care.
This breakthrough demonstrates the immense potential of artificial intelligence and machine learning to revolutionize cardiovascular care. By integrating diverse data sources and uncovering complex patterns, these advanced analytical techniques can deliver highly accurate and personalized predictions – a crucial step towards truly precision medicine.
Broader Implications and Future Directions
While this study focused on predicting pacemaker needs after TAVI, the researchers believe their approach could be applied to forecast other post-procedural complications, such as paravalvular leaks or strokes. Additionally, the team is exploring the use of deep learning techniques to directly analyze CT scan images, potentially eliminating the need for manual feature extraction and further improving predictive accuracy.
As the field of cardiovascular medicine continues to embrace the power of AI and data-driven decision-making, tools like this machine learning model for TAVI pacemaker prediction will become increasingly valuable. By empowering clinicians with personalized risk assessments and guiding more informed treatment decisions, these innovations have the potential to enhance patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and transform the way heart disease is managed worldwide.
Author credit: This article is based on research by Amine El Ouahidi, Yassine El Ouahidi, Pierre-Philippe Nicol, Sinda Hannachi, Clément Benic, Jacques Mansourati, Bastien Pasdeloup, Romain Didier.
For More Related Articles Click Here
